FoamGenerator
The foam generator is a command line tool to generate spray, foam and bubble particles in a postprocessing step which improves the visual realism of the simulation results. It takes a sequences of particle files and generates a sequence of new particles representing spray, foam and air bubbles. These additional particles are advected using the velocity field of the fluid. Below are two examples which were generated using the foam generator tool:
|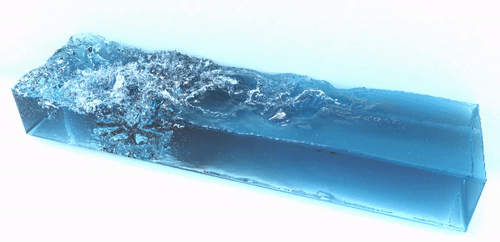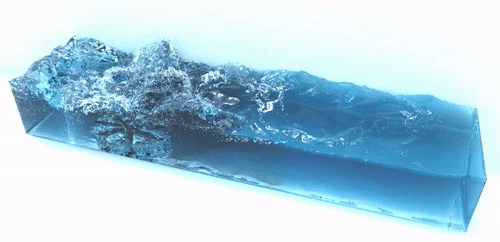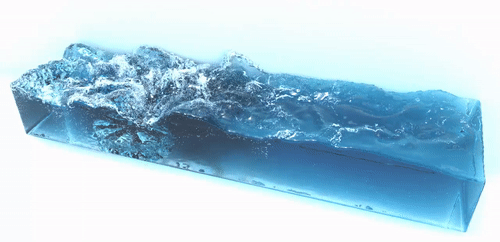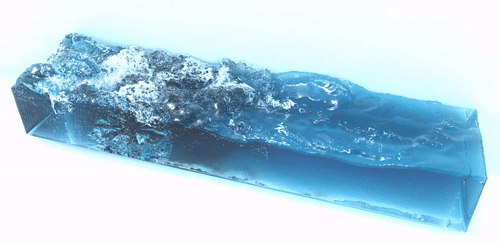 |
| |
| —- | —- |
|
| —- | —- |
The tool implements the methods of:
Markus Ihmsen, Nadir Akinci, Gizem Akinci, Matthias Teschner. Unified spray, foam and air bubbles for particle-based fluids. The Visual Computer 28(6), 2012
Jan Bender, Dan Koschier, Tassilo Kugelstadt and Marcel Weiler. Turbulent Micropolar SPH Fluids with Foam. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 25(6), 2019
Parameters for foam generation
The foam generator first analyzes the complete simulation data before the generation starts. During this analysis the tool determines the maximum values per frame for the potentials as proposed by Bender et al. [2019]. The resulting values are used for an automatic configuration of the parameters –ta, –wc, –vo and the limits. If you want to set these parameters manually (like in the original method of Ihmsen et al. [2012]), then you have to use the command line parameter “–no-auto” and set the parameters –ta, –wc, –vo and –limits.
Bounding box
Moreover, it is possible to define a bounding box for the foam particles. Foam particles are advected only using the velocity field of the fluid. However, there is no boundary handling since this would be quite expensive. Hence, particles can go through the boundary. A simple solution is to define a bounding box and clamp the particles which leave the box or kill these particles or steal their lifetime.
Frame rate
We recommend to generate the fluid sequence with 50 fps. Therefore, by default the time step size of the generator is set to 0.02s. If you use another frame rate, you have to adapt this parameter.
Further parameters
The parameter –buoyancy defines the buoyancy of air bubbles. Higher values let them go up faster.
The parameter –drag defines the coefficient of a drag force between the fluid particles and the foam particles.
The parameter –foamscale defines how many foam particles are generated per frame.
The parameter –lifetime defines the minimum and maximum lifetime of the foam particles in seconds.
The parameter –skipframes allows you the skip frames when writing the foam data, e.g. if you have a 50fps fluid sequence and want to write a 25fps foam sequence.
The parameters –splittypes and –splitgenerators can be used if you want to split the output in spray, foam and air bubble particles.
Command line options:
-h, –help: Print help
-i, –input arg: Input file (partio)
-o, –output arg: Output file (partio or vtk)
-q, –query: Query mode: determines max/avg values
–no-auto: Disable automatic mode. Limits and factors ta, wc, vo must be set manually.
–splittypes: Output each foam type to a different file
–splitgenerators: Output different foam files depending on which potential generated the foam. Overrides –splittypes.
-s, –startframe arg: Start frame (default: 1)
-e, –endframe arg: End frame
-r, –radius arg: Particle radius (default: 0.025)
-t, –timestepsize arg: Time step size (default: 0.02)
-k, –kernel arg: 0: Cubic spline, 1: Ihmsen et al. 2012 (default: 0)
-l, –limits arg: Limits (min/max) for potentials (trapped air, wave crest, vorticity, kinetic energy) (default: 5,20,2,8,5,20,5,50)
–lifetime arg: Lifetime (min/max) (default: 2.0,5.0)
-b, –buoyancy arg: Buoyancy (default: 2.0)
-d, –drag arg: Drag (default: 0.8)
–ta arg: Trapped air factor (default: 4000)
–wc arg: Wave crest factor (default: 50000)
–vo arg: Vorticity factor (default: 4000)
–bbsize arg: minimum and maximum coordinates of and axis aligned bounding-box (minX, minY, minZ, maxX, maxY, maxZ)
–bbtype arg: chose how the bounding-box is used [kill | lifesteal | clamp]. Use in combination with –bbsize.
–skipframes arg: number of frames to skip when writing foam (default: 0)
-f, –foamscale arg: Global multiplier for number of generated foam particles (default: 1000)
Example:
FoamGenerator -s 1 -e 500 -r 0.025 --foamscale 1000 -i output\DamBreakModelDragons\partio\ParticleData_Fluid_#.bgeo -o output\DamBreakModelDragons\foam\foam_#.bgeo